These initiatives are in-progress and associated documents, report, software and other outputs are expected to be released by end of 2026.
Agronomic Field Studies
Our primary research program centers on performing small-scale agronomic field studies. In the first phase of this research, we are growing multiple crops on solar and non-solar control plots to assess the relative impact of the shading conditions. Out this research, crops with suitable interest will be studied in larger planting areas for more accurate statistically robust results across range of conditions (e.g. panel spacing and variations of panel design).
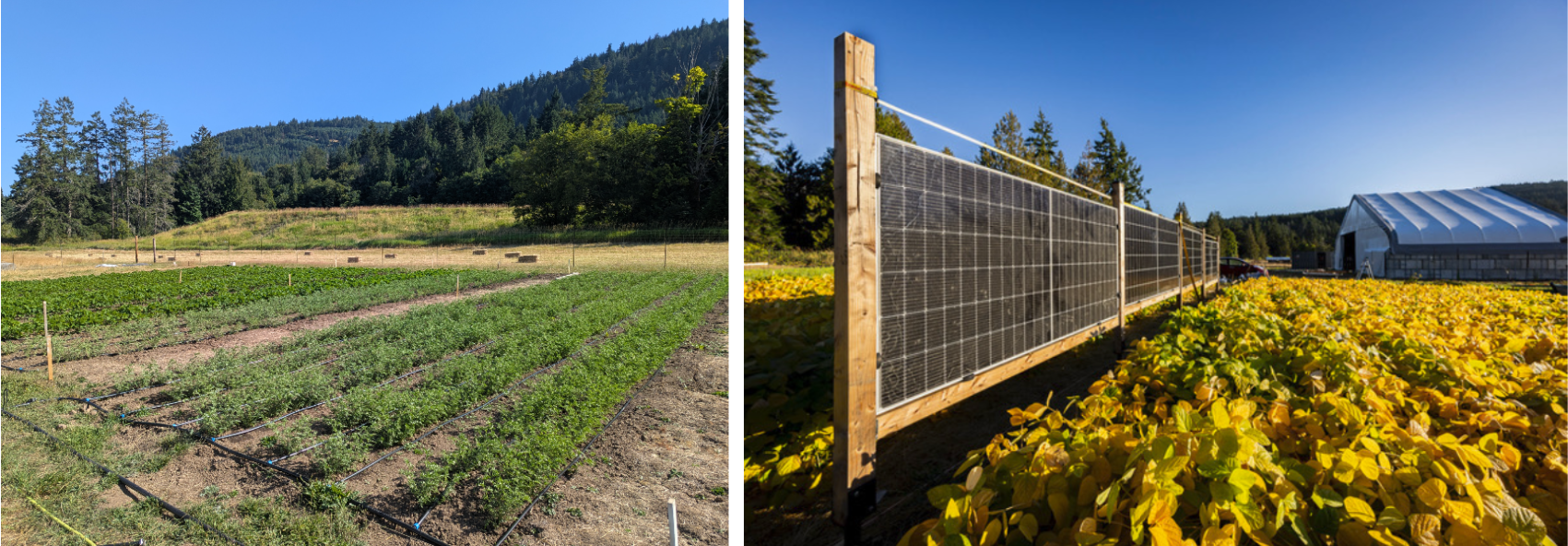

High-nutrititional value crops
We have started working with soy beans and chickpeas, candidates for 2026 trial crops alongside arrays.

Ecovoltaic Simulation and Design Software
The microclimate created by panels is interesting in several dimensions. The portion of sun in terms of angles and times of day received by the solar panels reduces water losses compared to no panel conditions. At the same time, the portion received by the plants creates conditions that cool the solar panels compared to having no plants in proximity. These basic effects are in turn effected by prevailing air pressure, wind, and ambient temperature.
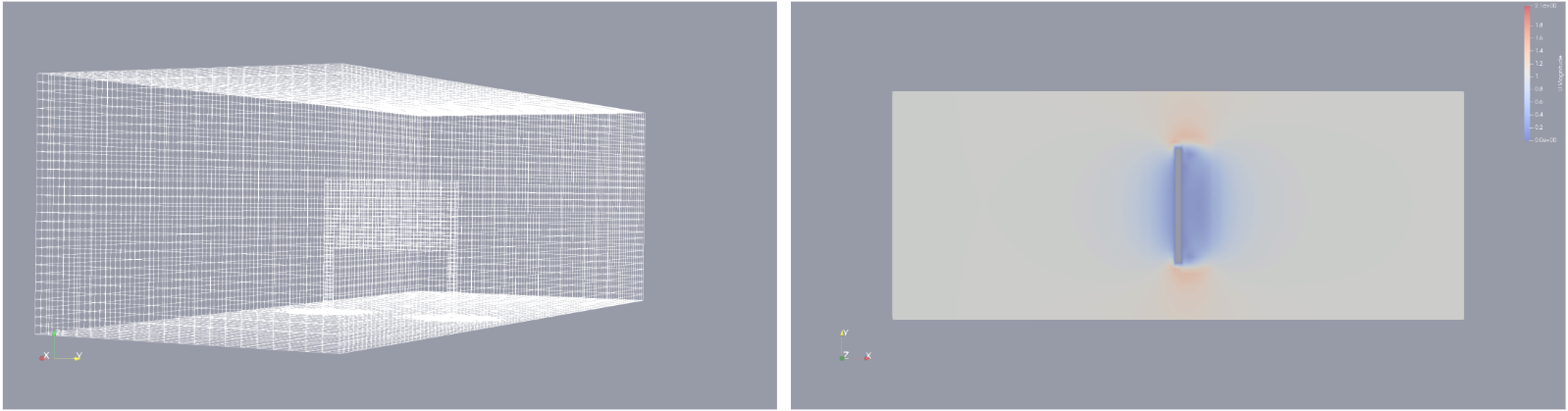
A concept of digital twin we are exploring seeks to assemble a integrated model out of component models that are concerned with lighting, air flow, thermal exchange, and crop growth. By pursuing this project in parallel to the field studies, we can collect data that allow us to assign accuracy bounds and in places improve and tune these models.
Open Hardware Designs
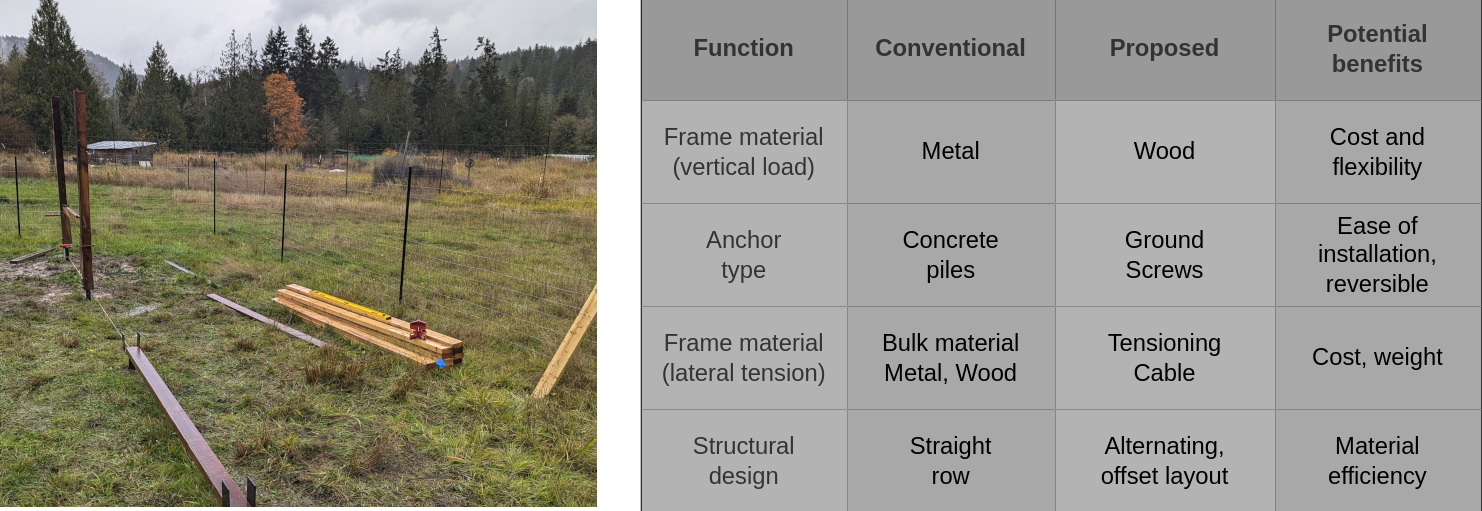
Low-cost, accessible design of vertical bifacial array
Our present project is based on an agrivoltaic architecture that has been designed for accessibility. We pursue accessibility in a number of dimensions, including cost of materials, use of commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) materials, and ease of construction.
Low cost, accessible design of agronomic instrumentation
We are developing a low-cost, solar-battery powered agronomic sensor station that communicates wirelessly with a nearby collector at the test site via low-power LoRa physical protocol. The collector can be run on a raspberry pi or modestly powered single board computer and handed off via cellular modem, satellite internet, or conventional internet.